What is a cookie?
All websites use cookies. Cookies are great for improving your website’s functionality. They are great for collecting insights for your analytics. Or for retargeting so you can spend your marketing budget in a smart way. But there are different types of cookies, and specific rules for how they can be used. This article walks you through what cookies are and whether they may pose a risk to your compliance.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small text files that your website stores in your visitor’s browser. These files typically contain information about your visitor’s preferred language settings or location, but can store a wide range of information including personally identifiable information. The information is passed between the browser and the webserver which makes it possible for the website to recognize your visitor’s settings when they return to your site!
What are cookies used for?
Cookies basically perform two actions: they improve your visitor’s experience of your website and they track your user’s behavior on your site. They are designed to contain specific information about your user’s visit on your site.
For example, if you have a web shop and your user puts items in the shopping cart, a cookie will remember that item as the user continues to browse. Or, your user may prefer another language variation on your site – a cookie will store that information. When the visitor returns to your site, your website reads the information in the cookies and remembers the preferences.
However, cookies are also designed to track users’ on your website and across the web. A lot of companies which provide your website with software solutions (analytics, widgets, add-ons, CRMs) set cookies through your site. These cookies are most often used not only for your benefit but also for creating user profiles for marketing purposes. This tracking may be an intrusion of your visitors’ privacy and is subject to data protection regulations such as the ePrivacy Directive, GDPR, and CCPA.
What are the different types of cookies and what do they do?
There are two main types of cookies: session cookies and persistent cookies.
What are first-party, second-party, and third-party cookies, and how do they differ?
When it comes to cookies, the main distinction lies in where they originate and how they are used.
So who places cookies on your user’s device? Understanding the difference between first-party, second-party, and third-party cookies is important for both website owners and users, as each type has unique purposes related to tracking, personalization, and advertising.
Here’s a breakdown of each:
First-party cookies
These cookies are set by the website you are currently visiting. Only that website can read the information stored in the cookie. First-party cookies are commonly used for things like remembering user settings or preferences on the site.
Second-party cookies
A second-party cookie is essentially a first-party cookie from another website. It occurs when one company shares its data (such as through a partner relationship) with another site to help with tracking and marketing efforts. This setup is less common but can be useful for data-sharing agreements.
Third-party cookies
Third-party cookies are set by a domain other than the one you’re currently visiting. These cookies are commonly used by advertisers and other third-party organizations to track users across different websites. They collect data for targeted advertising, social media integration, and analytics purposes. Read more about third-party cookies
- Google Analytics
- Facebook Pixel/like buttons
- YouTube (video embeddings)
- Widgets from your CMS
- Advertising networks/partners
How to check cookies used by your website?
Right click on the website and press Inspect > > Application > Storage > Cookies in order to get a list of the cookies being placed on the specific browser. Doing so in Incognito will give you accurate results, as the picture won’t be influenced by previous consent choices. This is also a good way of checking whether your website places any unnecessary cookies before user consent is given / rejected.
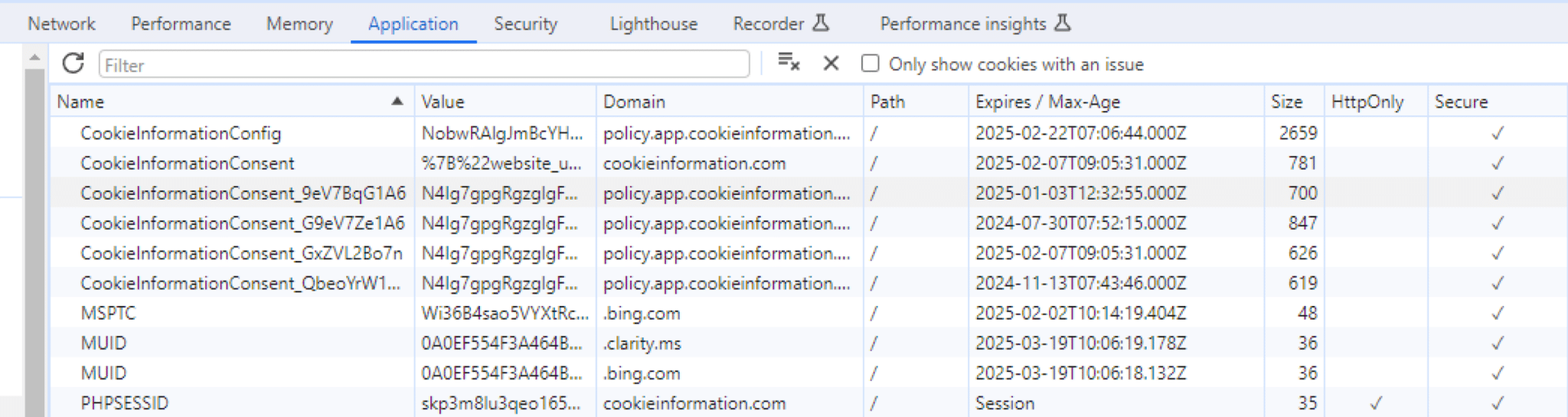
Do cookies pose a privacy risk?
Are third-party cookies being phased out?
This move is part of a larger trend among browser vendors responding to increasing concerns about user privacy and data protection. Other browsers like Mozilla Firefox and Apple’s Safari have already implemented stronger third-party cookie restrictions.
If you’re looking for a consent management platform that collects user consents and is compatible with Consent Mode v2, try Cookie Information’s cookie banner – compatible with your CMS of choice and free to try for 30 days.
Try Cookie Information - the website cookie banner that supports your marketing goals.
PRODUCTS
